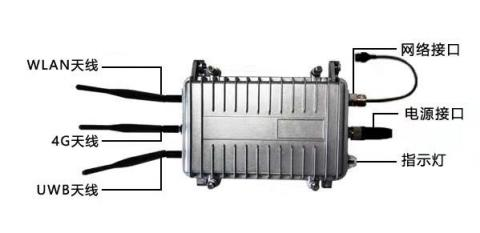
UHF 在医疗行业的应用
FDA的测试表明,为了获得可测量的温度升高,物品必须在最长读取时间内以非常接近的范围曝光很长一段时间,——通常在项目级的RFID实施中没有这种情况。
安全性:生物制品
谬论:UHF频率有加热药物的能力,并可能改变药物的化学成分,给消费者带来可能的安全问题。
真实的场景:
在典型的RFID项目级别部署中,物品距离读写器器大约18~24英寸,并且该物品在读写器区域保持少于10秒。为了在最近的测试中获得一个可测量的温度升高,物品在非常接近的范围(离读写器仅几英寸)暴露在UHF能量中,达一个或多个小时-这不是真实的RFID实施场景。
事实:
确实,UHF和HF的能量能够被某些物质吸收,因此能够提高某一物质的温度。然而,由于极低的功率,物质需要暴露在频率上数小时以上。美国规范标准的UHF读写器的输出功率不大于1W,而在欧洲的UHF 读写器的输出功率则仅仅只是0.5W。
这些数字分别是100瓦灯泡的1/100和1/200的功率。为了提高温度,一种物质需要留在读写器范围里停留几个小时。然而,在实际利用RFID的应用中,这种情况不会发生–在传送带上的药瓶和药瓶会暴露在读写器区域仅仅几秒钟--时间很短不足以有效或可测量地升高任何物品的温度。
美国FDA进行的一项主要涉及计算机建模和有限物理测试的研究证实了这一说法。
根据一个不可行的最坏情况而不是实际的部署指标,FDA的研究表明,放置距离超高频RFID天线5厘米(2英寸)的14.4厘米(5.6英寸)距离的胰岛素在读写器持续传输能量一小时后将升温1.7°C(3°F)。
然而,在典型的物品级RFID项目应用中,物品只会暴露在读写器传输的几秒钟内,并且距离阅读器的平均距离为46-60厘米(18-24英寸)。美国FDA的测试表明,为了获得可测量的温度升高,物品必须在最非常接近的读写器的读取范围内暴露很长一段时间 ---通常在物品级的RFID项目实施中不会发生。
来自该协会进行的实际实验室环境中非正式测试的结果进一步验证了FDA计算机建模的结果。在一个简单的实验中,环境温度为72°F(22.2°C)的生理盐水溶液连续暴露在非常近的范围,从RFID超高频阅读器获得全部功率。它需要24小时持续暴露于UHF能量的盐水中,以加热1.7°C(3°F)---这对于实际的RFID部署和工作来说不会发生。
相比之下,HF阅读器使用更高的功率。在美国,最大高频阅读器瓦数是2瓦,在欧洲,高频阅读器可以输出高达10瓦。 尽管阅读器功率有所增加,但由麦哲伦科技公司在高频阅读器上进行的测试产生了与FDA测试和该联盟的非正式测试相同的结果。 为了使温度上升一度,必须将Tunnel Reader中的持续能量暴露16小时。在实际的RFID项目级实现中,需要产生可测量的热增量的度量标准不会发生。
安全性不是频率的函数。UHF系统可以为敏感数据提供与基于HF的系统相同级别的安全性。Gen2提供了内置的安全措施,包括32位访问和杀死密码保护,传输数据的覆盖编码等等。
除了这些标准之外的额外安全性,由客户和应用程序需求驱动,可轻松集成到超高频RFID系统中——不受频率限制。
UHF vs. HF:谬论与事实
|
高频HF RFID 与超高频 UHF RFID 的区别明细 |
||
|
参数对比 |
谬论 |
事实 |
|
液体与金属环境 |
在装有液体的容器以及金属物体上,只有高频表现很好;这两种应用形态已经在医疗领域中大量应用 |
在液体中或者液体表面,超高频可以表现很好;当超高频电子标签接触金属物体时,标签会把金属当做自己天线的一部分,所以会表现的很出色 |
|
读取范围控制 |
在一些要求苛刻的项目中,只有高频才能有效控制都区范围 |
选择合适的天线以及降低读写器发射功率,超高频能够很精准的控制读取范围 |
|
安全级别 |
在医疗制药领域,只有高频的加密才能保证标签数据的安全级别 |
安全系数与频段无关,超高频系统可以提供与高频系统一个级别的安全保证 |
|
标签尺寸 |
只有高频标签才能够轻松应用于很小的物品中 |
标签尺寸影响读取距离,大的超高频标签是为了满足远距离的识别,在一些近距离的应用中,超高频标签可以很小,小到可以装进一个瓶盖子 |
|
标签形态 |
在制药领域,只有高频标签才能根据需求提供丰富、灵活的标签形态 |
超高频标签的天线可以使用导电油墨制作,而不是像高频标签需要很多蚀刻金属线圈;因此,超高频标签提供灵活的产品形态,而且可以简单的、低成本的集成到包装里面以弯曲的形式附着在一个瓶子的表面 |
|
标签的密集堆叠 |
当标签跟标签挨的很紧密时,只有高频标签才能被读到 |
超高频标签细小的天线可以减少标签之间的干扰,这样确保密集堆叠的超高频标签也能被读到,即使是被完全接触的标签 |
|
电磁干扰 |
在嘈杂的射频环境中,例如叉车、无线网或者其他设备发出的电磁干扰,高频不易受到干扰,可以很好的工作 |
在一些应用中,基于近场的物理特性,超高频在嘈杂的噪声环境中,防止信号被渗透、破坏 |
|
技术成熟度 |
更安全的技术选择源于更成熟、很多的应用已被现场证明 |
如今,在全球最大的制药现场已经证明,超高频只是才刚刚起步,在不久的将来,超高频将会提供更多的创新应用、以及低成本的技术;不像高频,技术已完全饱和,达到了技术天花板 |
|
读取速率 |
在理想的企业级应用环境中,高频能做到读速200tags/s |
超高频针对企业应用需求建立了标准,标签识读率能达到1000tags/s,满足最大的仓库和货架上的应用,不影响仓库的吞吐量 |
|
标准 |
高频提供全球唯一的RFID标准 |
超高频提供了一个真正的全球标准,旨在提供无线网络的互操作性。高频提供单一频率,很多标准无法兼容 |
|
在项目层面,超高频能 |
在测试中,若需要提高物品温度,物品需要暴露在超高频磁场中,距离发射源差不多2英寸的地方,同时超高频设备用最大发射功率工作1小时或者更长时间,而在真实的应用中,典型距离为18英寸、也不是全功率工作 |
|
英译原文:
The FDA tests illustrate that, in order to obtain a measurable increase in temperature, items must be exposed at very close range at maximum reader power for a long period of time — criteria typically not found in item level RFID implementations.
Safety: Biologics
The myth: The UHF frequency has the capability to heat medications and possibly alter the chemical makeup of the medication, creating possible safety issues for consumers.
The reality:
In the typical RFID item level deployment, items are approximately 18 to 24 inches from the reader, and the item remains in the reader field for less than 10 seconds. In order to obtain a measurable rise in temperature in recent tests, substances were exposed to UHF energy at a very close range (just a few inches from the reader) for one or more hours — not a feasible realworld implementation scenario.
The facts:
It is true that UHF, as well as HF energy, is absorbed by certain materials and is, therefore, capable of increasing the temperature of a given substance. However, due to the extremely low power, substances would need to be exposed to the frequency for many hours. UHF reader output in the U.S. can be no greater than 1 watt, and in Europe, it is 0.5 watt.
Those amounts are 1/100th and 1/200th of the power in a 100-watt light bulb, respectively. In order to raise the temperature, a substance would need to remain in the reader field for hours. However, in reallife RFID applications, that does not occur — bottles or vials of medication and cases on a conveyor belt are exposed to the reader field for just a few seconds — not long enough to effectively or measurably raise the temperature of any item.
A study primarily involving computer modeling with limited physical testing conducted by the U.S. FDA validates this statement.16 Based on a non-feasible worst-case scenario instead of actual deployment metrics, the FDA study states that a 14.4 cm/5.6 in. vial of insulin placed 5 cm/2 in. away from a UHF RFID antenna will heat up 1.7°C/3°F after an hour of continual energy transmission from the reader. However, in the typical item level RFID application, items would only be exposed for seconds to the reader transmission, and would be an average distance of 18 – 24 inches/46 – 60 cm from the reader. The FDA tests illustrate that, in order to obtain a measurable increase in temperature, items must be exposed at very close range at maximum reader power for a long period of time — criteria typically not found in item level RFID implementations.
The results from informal testing in an actual lab environment conducted by this consortium further validate the results from the FDA computer modeling. In a simple experiment, a saline solution at ambient temperature 72°F (22.2°C) was continuously exposed at extremely close range to full power from an RFID UHF reader. It required 24 hours of constant exposure to UHF energy for the saline to heat up 3°F/1.7°C — an unlikely scenario for a real-world RFID deployment.
HF readers, by comparison, use a much higher wattage. In the U.S., maximum HF reader wattage is 2 watts, and in Europe, HF readers can put out up to 10 watts. In spite of the increase in reader power, a test conducted by Magellan Technology on HF readers produces the same results as the FDA tests and this consortium’s informal test. An item had to be exposed to continual energy in the company’s Tunnel Reader MSTRP 5050 for 16 hours in order to obtain a one-degree temperature rise. The metrics that were required to produce a measurable increase in heat would not occur in real-world RFID item level implementations.
Security is not a function of frequency. UHF systems can provide the same level of security for sensitive data as an HF-based system. Gen 2 provides built-in security measures, including 32-bit access and kill password protection, cover-coding of transmitted data, and more.
Additional security beyond those standards, driven by customer and application requirements, is easily integrated into a UHF RFID system — there is no limitation due to frequency.
深圳市铨顺宏科技有限公司作为ThingMagic代理商不仅提供优质的ThingMagic超高频rfid读写模块,ThingMagic超高频rfid读写器,超高频rfid天线,更提供一对一的售后技术支持,配合运营商、集成商将ThingMagic超高频rfid设备应用到rfid服装管理,rfid档案管理,rfid叉车管理,rfid仓储物流管理等领域。
深圳铨顺宏将竭诚为您服务,您可以点击网页右上角的在线客服联系我们
相关资讯
- ThingMagic 新产品Elara USB读卡器和EL6e智能模块即将上市
- 基于超高频RFID技术的wms仓库管理系统
- ThingMagic中国区RFID技术及应用分享会之UHF RFID 技术与性能分析
- ThingMagic中国区RFID技术及应用分享会之RFID技术在智慧工厂中的应用
- ThingMagic中国区RFID分享会之“超高频RFID技术与应用”
- 铨顺宏主办的"第四届 Thingmagic中国区 RFID技术及应用分享会”在深圳市南山区朗山酒店朗逸厅顺利举行
- 铨顺宏联办"2018年第三届物联网产业发展与技术合作研讨会"暨"西安移动NB-IoT高峰论坛"即将召开
- 2018深圳国际工业物联网应用研讨会之“物联网技术在汽车制造领域的应用”
- 铨顺宏科技2018年第十届国际物联网博览会夏季展精彩回放
- 铨顺宏科技荣幸受邀,参加“2018中国(国际)RFID产业应用及创新论坛"
同类文章排行
- 邀请函|铨顺宏科技诚邀您莅临深圳高交会(CHTF 2024)
- 2023《射频识别(RFID)技术与标准化蓝皮书》正式发布
- 2023年第五届物联网产业发展与技术合作研讨会
- 热烈祝贺铨顺宏正式担任广州市物流技术与应用协会理事单位
- 铨顺宏携新产品亮相2023第十一届中国西部电子信息博览会!
- 铨顺宏RFID:战备物资定制智能RFID仓储系统软件
- 铨顺宏RFID:试卷管理中RFID技术智能系统发挥着什么样的作用
- 铨顺宏RFID:图书馆系统服务项目的科学研究
- RFID叉车仓储管理应用
- 铨顺宏RFID:建筑工地人员管理解决方案
最新资讯文章
您的浏览历史